In this C programming class, we will cowl the C resolution-making constructs so as C if, if-else, and the switch-case assertion. It is additionally identified as conditional programming in C.
C Decision Making Statements
In your life, you experience conditions the spot you need to choose be it your number one suppers dish or the shade of your new car. In C programming also, odds are you’ll experience such conditions the spot it’s fundamental to decide.
The circumstances in the C language will help you.
C principally gives the following three types of restrictive or goal-making assemble.
- if statement
- if-else statement
- switch case
if Statement in C Programs
The if statement facilitates testing a selected situation. If that situation is true, then a selected block (enclosed under the if) of code will get executed.
This flowchart will aid you.
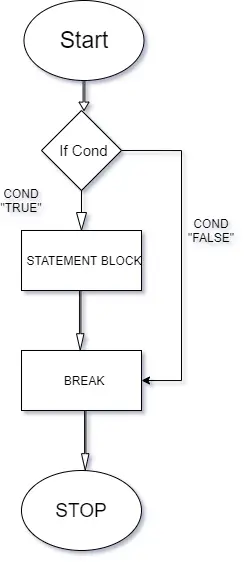
Now we’ll see an easy program utilizing if statement.
Example 1: Program to find out the higher quantity between two numbers.
Flowchart:
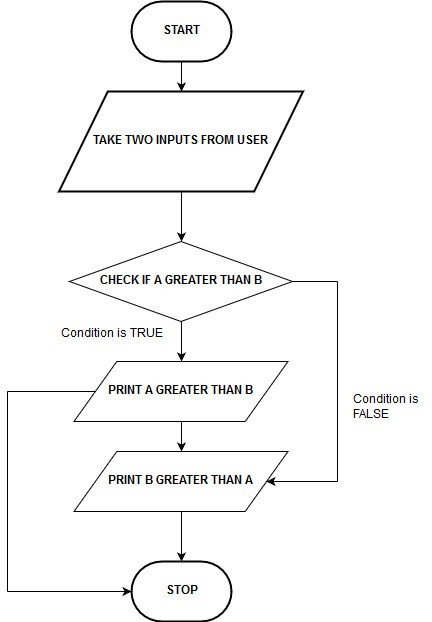
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start. Step 2: Take two inputs (a and b) from the person. Step 3: If a is higher than b then go to step 4 in any other case go to step 5 Step 4: Print a higher than b Step 5: Print b higher than a Step 6: Stop.
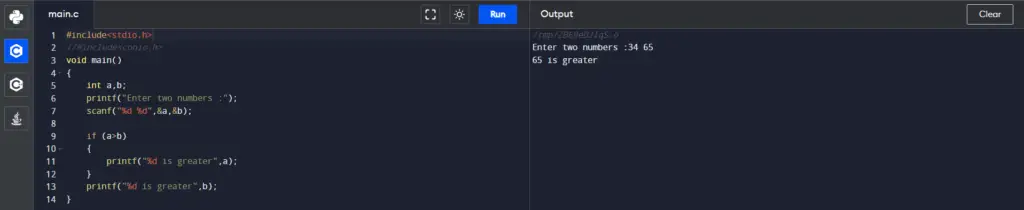
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Enter two numbers :");
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
if (a>b)
{
printf("%d is greater",a);
}
printf("%d is greater",b);
retutn(0);
}Output:
2. if-else Statement in C
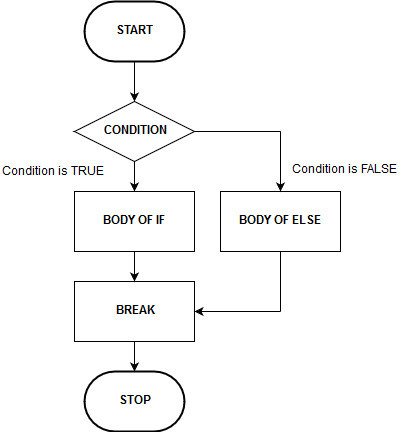
The if attestation functions admirably, in any case, if you need to work with additional variables and additional information, the if-else explanation comes into play.
ue,
In the if proclamation, only one square of code executes after the circumstance is true.
But in the if-else explanation, there are two squares of code – one for managing the achievement and different for the disappointment situation.
This flowchart will aid you to get it.
Syntax:
if(situation)
//Statement block
else
//Statement block
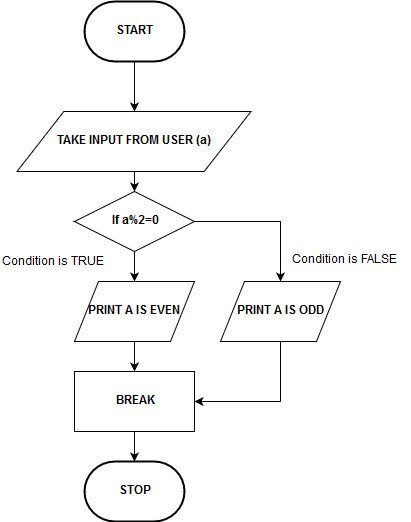
Example 2: Program to find out whether or not a quantity is odd or even.
Flowchart:
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start. Step 2: Take enter from the person. Step 3: Check condition. If the rest is zero then go to step 4 else go to step 5 Step 4: Print a is even and go to step 6 Step 5: Print a is odd Step 6: Stop
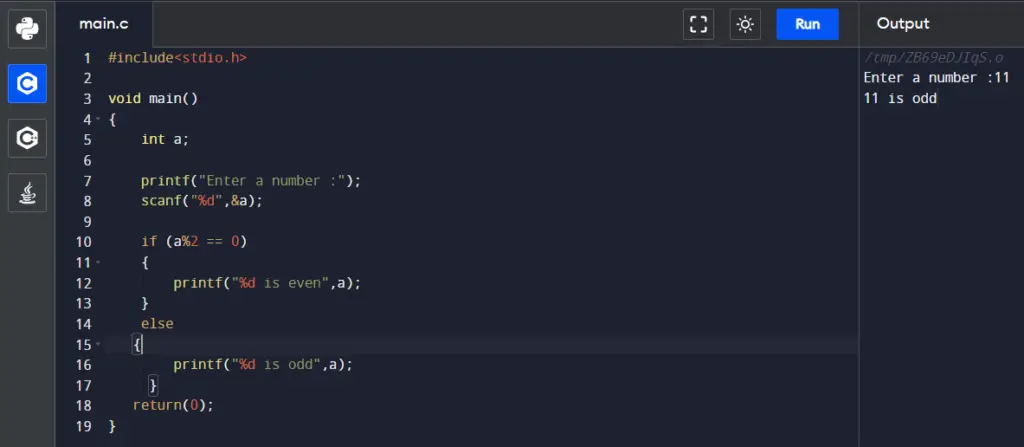
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a;
printf("Enter a numbers:");
scanf("%d",&a);
if (a%2 == 0)
{
printf("%d is even", a);
}
else
{
printf("%d is odd", a);
}
return(0);
}Output:
You can use a number of if-else statements which are known as “nested if-else” statements. It is no totally different than the one above you should use varied if-else statements in this order. Just preserve in thoughts that the sequence ought to finish with a final else assertion, not if statement.
3. Switch-Case Statement in C
When you need to execute a number of statements under one operation, for there Switch-case comes into play.
There are a number of instances beneath one switch statement.
Syntax:
switch(variable)
case n1:
//1Statement block;
break;
case n2:
//2Statement block;
break;
.
.
.
case n:
//Statement block;
break;
Here the variable is taken from the person as enter.
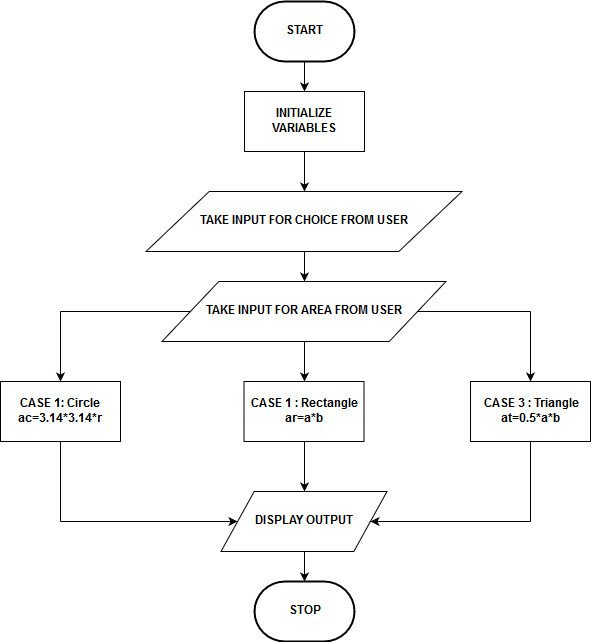
Example 3: Program to calculate the area of a rectangle, circle, or triangle by taking the person’s selection.
Flowchart:
Algorithm:
Step 1: Start Step 2: Initialize variables Step 3: Take enter for selection and then for space variables from the person Step 4: Case 1: Circle: 3.14 *3.14*r Case 2: Rectangle: ar =a * b Case 3: Triangle: at =0.5* a *b Step 5: Display output in accordance with case Step 6: Stop
Source Code:
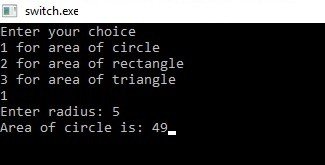
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int ac, ar, at, r, a, b, selection;
printf("Enter your choice”);
prinft("A for area of circle \n”);
printf("B for area of rectang \n”);
printf("C for space of triang 'n");
scanf("%c",&selection);
switch(selection)
{
case A:
printf("Enter radius: ");
scanf("%d",&r);
ac=3.14*3.14*r;
printf("Area of circle is: %d",ac);
break;
case B:
printf("Enter the length and breadth:");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
ar=a*b;
printf("Area of the rectangle is: %d", ar);
break;
case C:
printf("Enter value of base and height: ");
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
at=0.5*a*b;
printf("Area of triangle is: %d", at);
break;
}
return(0);
}Output:
Related Posts
- How to compare dates in java|algorithm with source code
- Java roll dice 10000 times with algorithm and source code
- Write a Java program that displays the number of characters, lines, and words in a text
- Write a Java program that reads a file and displays the file on the screen with a line number before each line
- Write a Java program that reads a file name from the user, then displays information about whether the file exists, readable, writable, type of file, and the length of the file in bytes
- Java program to make frequency count of vowels, consonants, special symbols, digits, words in a given text
- Write a Java program for sorting a given list of names in ascending order
- Get Salesforce Answers