From this tutorial, you will be learning about the Python Copying module. It has a short learning curve when compared to other modules especially if you have read other topics.
Note: The syntax used in the below section is for Python 3. You may change it to use a different version of Python.
Copy Module in Python
Here we will see the different examples of using copy model.
What is Copy Module?
Copy Module_is a set of functions that are related to copying different elements of a list, objects, arrays, etc. It can be used to create shallow copies as well as deep copies.
The difference between shallow and deep copy operations got explained in a tutorial on Deep Copy vs. Shallow Copy in Python 3.
How does the Copy module work?
The syntax to implement Copy_Module is shown below
import copy copy.submodule_name(arguments)
To perform the shallow copy, you can use the following code:
import copy copy.copy(object_name)
For the deep copy, follow the below approach:
import copy copy.deepcopy(object_name)
In the next section, a few programs are implemented to demonstrate the Copy Modules in Python 3.
Create the shallow copy of a list:
Here is a simple program to demonstrate the Shallow Copy.
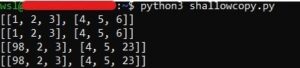
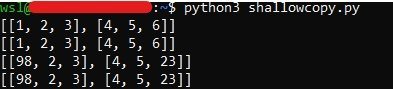
import copy a = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6] ] b = copy.copy(a) print(a) print(b) a[1][2] = 23 b[0][0] = 98 print(a) print(b)
The output will come as:
Create a deep copy of a list:
Check another program for Deep Copy operation.
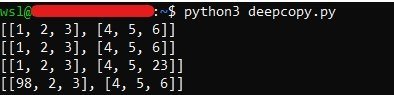
import copy a = [ [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6] ] b = copy.deepcopy(a) print(a) print(b) a[1][2] = 23 b[0][0] = 98 print(a) print(b)
The output will come as:
For more Wikipedia