From this tutorial, you may be studying about Python checklist Index technique. You will see how you can apply it to sequences with the assistance of examples.
Note: The syntax used in the beneath part is for Python 3. You can change it to every other variation of Python.
Python List Index Method
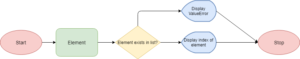
The Index operation is a built-in checklist technique that permits you to find out the index or place of a component in a sequence.
In different phrases, this technique searches for a component in the checklist and returns its index.
Its syntax is as follows:
List_name.index(<factor>)
It takes the factor as an argument and returns the index. Please notice that you could present any entry such as an inventory or a tuple or a substring.
See the beneath instance.
>>> myList = ['1', '11', 1, 'a', 'x', 1.1]
>>> myList.index(1)
2
>>> myList.index('x')
4How does the Index() operate work?
It takes one entry which is the factor for which you need the index or place as the output.
This technique searches for the factor in the checklist and returns the index that matches its worth else raising the ValueError error.
While looking for substrings, it raises the next error.
"Substring not found"
>>> first = 'Python is the language of the long run.'
>>> print(first.index('lang', 10))
14
>>> print(first.index('invalid', 10))
Traceback (most up-to-date name last):
File "<pyshell#34>", line 1, in <module>
print(first.index('invalid', 10))
ValueError: substring not discovered
>>>Using the improper factor
myList = [2,3,4,5,6] myList.index(1)
The output is:
Traceback (most up-to-date name last): File "C:PythonPython35test.py", line 3, in <module> myList.index(1) ValueError: 1 is not in checklist
Find the factor index in a tuple
myList = [2,3,(3,4),5] print(myList.index((3,4)))
The outcome is:
2
For more Search Wikipedia