From this tutorial, you’ll be studying Python checklist Sort by a key technique. You will see how to use it with lists with the assistance of examples.
Note: The syntax used in the beneath part is for Python 3. You can change it to another variation of Python.
Python List Sort
Here you will learn, how to sort the element from the list with examples.
List Sort Method:
The sorting technique performs the sorting of checklist components in both ascending and descending routes. Its syntax is as follows:
List_name.sort(key = …, reverse = ...)
When the sort() will get known without arguments, it kinds in ascending order by default. It doesn’t have a return worth.
It merely returns to the subsequent line without returning any output.
Please be aware that it is not associated with the built-in sorted() operation. The sorting technique mutates or modifies a previous checklist whereas sorted() creates a new sorted sequence.
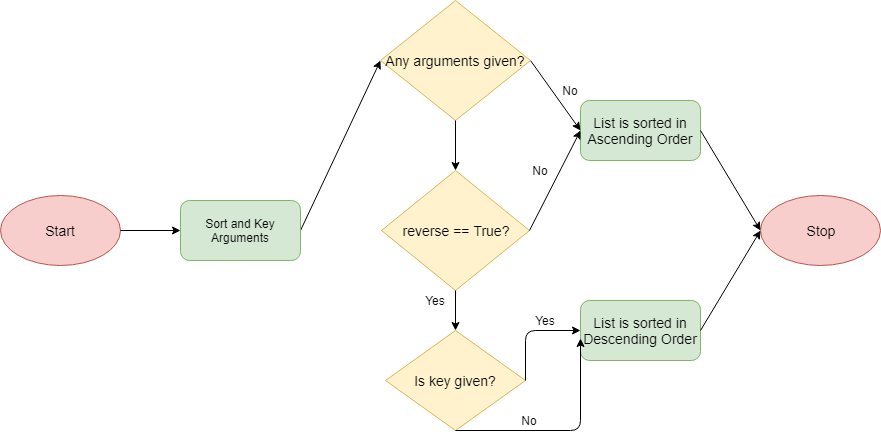
How does the Sort technique work?
When we name this technique, it traverses the checklist components in a loop and rearranges them in ascending order when there aren’t any arguments.
If we specify “reverse = true” as an argument, then the checklist will get sorted in descending order.
The main parameter is the steps that the tactic should undergo when sorting by way of a checklist of components. The worth given to the key will be an operation or an easy calculation and so on.
The flowchart for the mechanism is as follows:
Sort a checklist of numbers: Example – 1
a. Sorting a checklist of numbers in ascending order
Natural_numbers = [1,4,23,3,2,1,0,9,7] Natural_numbers.sort() print (Natural_numbers)
Output:
[0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 9, 23]
b. Sorting a checklist of numbers in descending order
Natural_numbers = [1,23,4,25,22,3,4,5,9,7,5] Natural_numbers.sort(reverse = True) print (Natural_numbers)
Output:
[25, 23, 22, 9, 7, 5, 5, 4, 4, 3, 1]
Sort a checklist of letters: Example – 2
a. Sorting a checklist of letters in ascending order
Vowels = ["a", "u", "i", "o", "e"] Vowels.sort() print (Vowels)
Output:
['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u']
b. Sorting a checklist of letters in descending order
Vowels = ["a", "u", "i", "o", "e"] Vowels.sort(reverse = True) print (Vowels)
Output:
['u', 'o', 'i', 'e', 'a']
Sort a checklist of strings: Example – 3
a. Sorting a checklist of strings in ascending order
Fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Tomato", "Grapes"] Fruits.sort() print (Fruits)
Output:
['Apple', 'Banana', 'Grapes', 'Tomato']
b. Sorting a checklist of strings in descending order
Fruits = ["Apple", "Banana", "Tomato", "Grapes"] Fruits.sort(reverse = True) print (Fruits)
Output:
['Tomato', 'Grapes', 'Banana', 'Apple']
Python List Sort by a key operate: Example – 4
a. Sorting a checklist by a key operation (ascending)
# Let's sort on the idea of 2nd factor
def keyFunc(merchandise):
return merchandise[1]
# Unordered checklist
unordered = [('b', 'b'), ('c', 'd'), ('d', 'a'), ('a', 'c')]
# Order checklist utilizing key
unordered.sort(key=keyFunc)
# Output the sorted checklist
print('Ordered checklist:', unordered)Output:
Ordered checklist: [('d', 'a'), ('b', 'b'), ('a', 'c'), ('c', 'd')]b. Sorting a checklist utilizing a key operation (descending)
# Let's sort on the idea of 2nd factor
def keyFunc(merchandise):
return merchandise[1]
# Unordered checklist
unordered = [('b', 'b'), ('c', 'd'), ('d', 'a'), ('a', 'c')]
# Order checklist utilizing key in the reverse route
unordered.sort(key=keyFunc, reverse = True)
# Output the sorted checklist
print('Ordered checklist:', unordered)Output:
Ordered checklist: [('c', 'd'), ('a', 'c'), ('b', 'b'), ('d', 'a')]For more, you can refer to GOOGLE and learn Python Tutorial here.